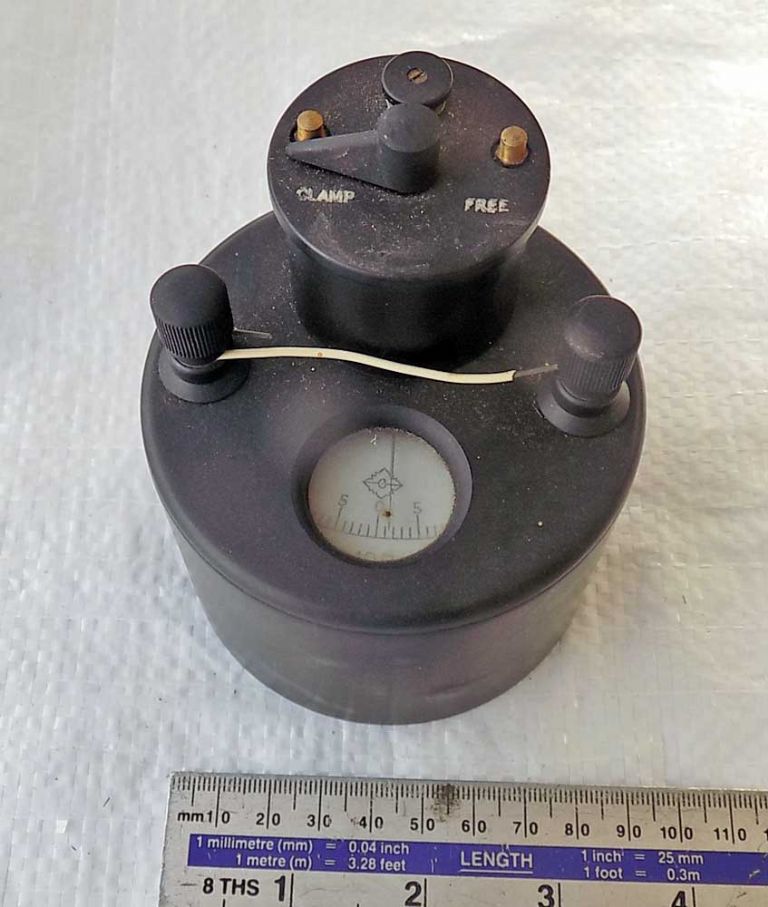
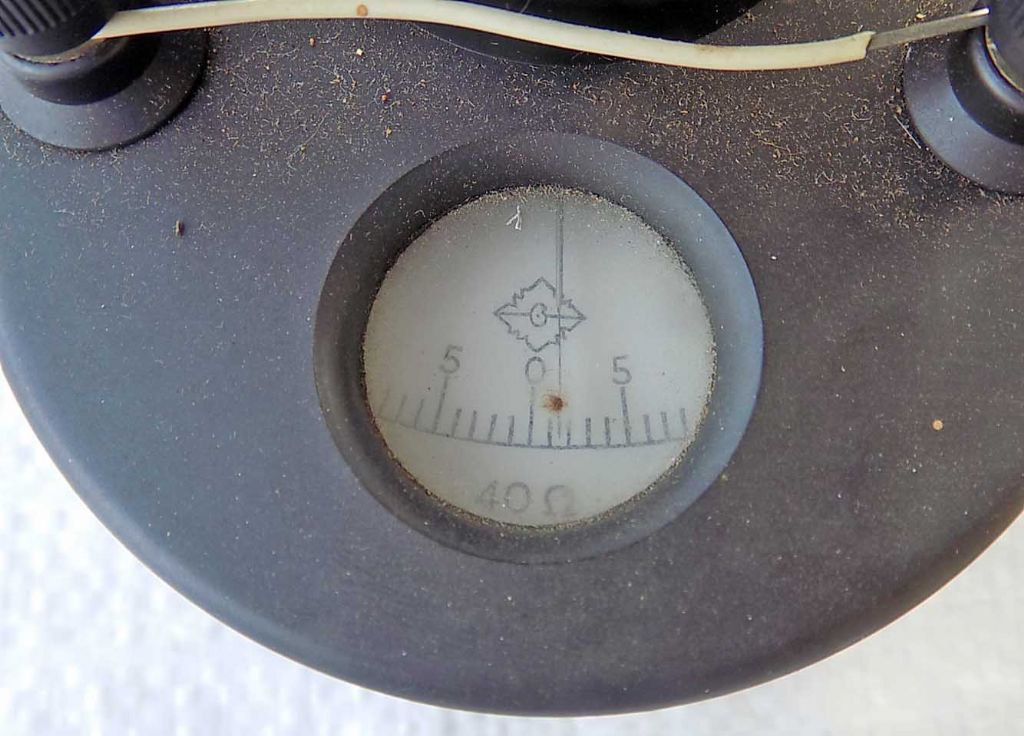
let's think about it from Einstein’s point of view.
E = mc^2
If light actually had zero mass, that equation would always equal zero!
Wave-particle duality applies?
There is clearly a lot of expertise being brought to bear on this topic, so much so that I am reluctant to dip my toe in the water, but I don't really understand the above post.
I was taught (many years ago ) that this equation meant (in simple terms) that an object of mass "m" contained (or was composed of) energy equal to m multiplied by c squared, where "c" was the speed of light, and that the energy and the mass were interconvertible. In the equation "c squared " is a constant and the mass of the light (if any ) is irrelevant.
I hesitate to say it, but has NDIY got confused and regarded "m" as the mass of the light? Or is it me?
Regards
Rod
 Simon Collier.
Simon Collier.